第一列
This project aims to develop a 10-qubit fluxonium superconducting quantumprocessor and advance key technologies for multi-fluxonium qubit chip design,fabrication, and testing. The project focuses on four main sub-projects:(1) Fabrication of multi-chip/wafer-scale fluxonium qubits, (2) Development of fluxonium-based quantum information chips, (3) Characterization of Josephson junction parameters and noise, and (4) Advanced fabrication techniques, including airbridge and flip-chip packaging. These efforts will enable the realization of a scalable fluxonium quantum processor with the potential to perform complex quantum information tasks.
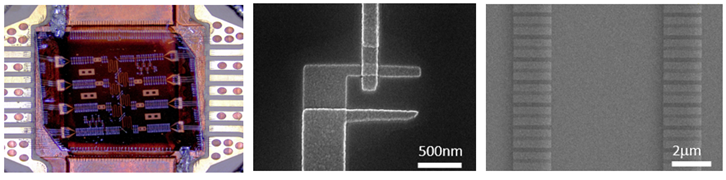
A fluxonium superconducting qubit chip containing six fluxonium qubits. The middle and right panels show scanning electron microscope(SEM) images of the core components of a fluxonium qubit: the single Josephson junction and the Josephson junction array.
-
Co-PI
-
Sheng-Shiuan Yeh(National Yang Ming Chiao Tung University)
-
Yong-Han Lin (National Institutes of Applied Research Taiwan Semiconductor Research Institute)
Two dimensional fluxonium superconducting qubits fabrication technique
- This technology aims to solve the following problems:
This technology aims to solve two key limitations: the difficulty of scaling three-dimensional fluxonium superconducting qubits to multi-qubit systems, and the relatively short energy-relaxation time typically observed in two-dimensional fluxonium qubits.
- Importance/Breakthrough:
In this work, we employ high-quality superconducting tantalum thin films with protective capping layers, combined with etching and electron-beam lithography techniques for fabricating Al/AlOx Josephson junctions. Using this approach, we have realized fluxonium superconducting qubits with energy-relaxation times as long as 3.3 ms.
- Relevance to the future research directions of the project:
This technology integrates advances in materials and fabrication processes while preserving the long of fluxonium qubits and the scalability advantages of two-dimensional chip architectures.
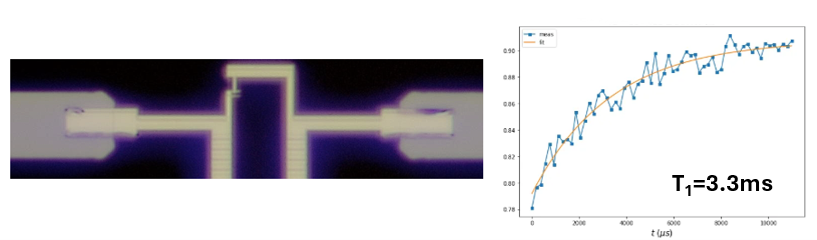
(Left) Optical microscope image showing the connection region in a fluxonium superconducting qubit where the tantalum thin-film capacitor interfaces with the Al/AlOx/Al Josephson junction and junction array. (Right) The fluxonium qubit fabricated using this structure exhibits a relaxation time of up to 3.3 ms.
